IO Cost Summary: Choosing Your Index
Understanding n vs N: The Dictionary Analogy
Webster's Dictionary (Sorted)
n = 171,476 words
From "aardvark" to "zyzzyva"
N = 1,000 pages
Physical book pages
Index size: Just N entries
First word per page + page number
Example: Page 42: "bicycle–bind"
To find "binomial": Check index, go to page 43, scan
RandomWebster's Dictionary (Unsorted)
n = 171,476 words
Randomly scattered across pages
N = 1,000 pages
Same physical book
Index size: All n entries
Every word + its page location
Example: "aardvark" p.847, "apple" p.203
Must track every single word individually
Definition: Clustered vs. Unclustered Indexing
How we physically organize data determines our retrieval cost:
- Clustered Index (The "Webster's"): The data itself is physically kept in sorted order. Because the data is sorted, we only need a sparse index (one entry per page).
-
Advantage: Optimal for range queries; data is naturally grouped together.
-
Unclustered Index (The "RandomWebster's"): The table data is stored in no particular order. The index must be dense (one entry for every row) to point to locations for each row (i.e., the index size depends on n and not N).
Sorted data (Clustered) compresses beautifully (N << n). Unsorted data (Unclustered) requires tracking every single record.
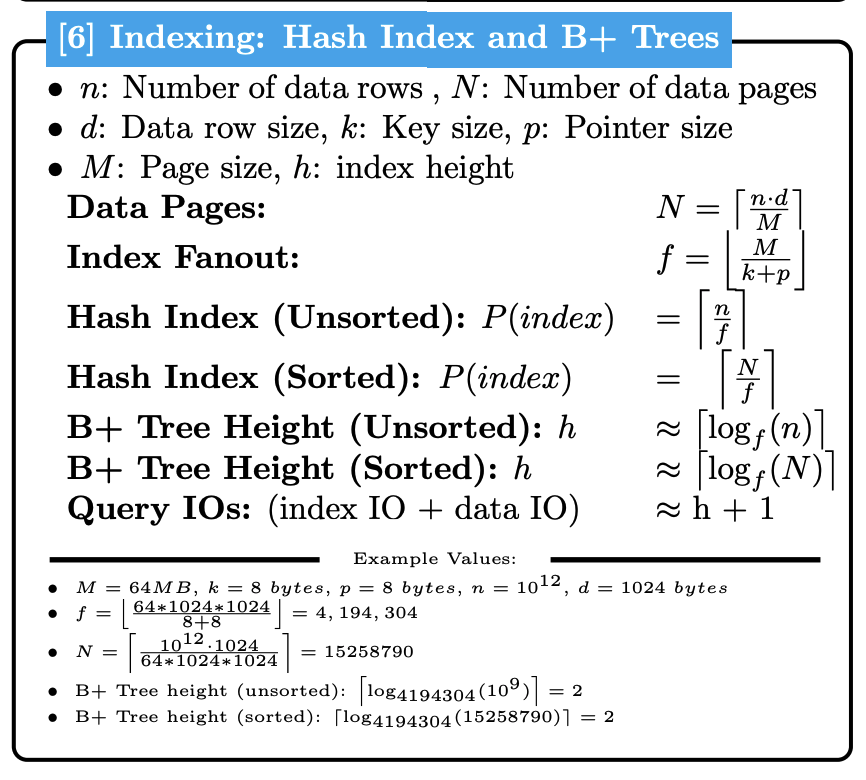
For detailed formulas and specifications, see the IO Reference Guide.