Locks: Foundations of Concurrent Control
Three Problems Locks Solve 🎯
3 Transactions (T1, T2, T3) doing some stock trading on X, Y accounts
🚫 Problem 1: Correctness
Lost Updates
❌ Without Locks:
T2: READ(x)=100
T1: WRITE(x=150)
T2: WRITE(x=130) ❌
→ T1's update lost!
✅ With Locks:
T2: [waits]→LOCK→READ(150)✓
⏱️ Problem 2: Long Calculations
CPU Idle During Complex Logic
❌ Serial Execution:
T2: Wait... then process data Y
T3: Wait... wait... then process data Z
→ Only 1 CPU core used!
✅ Parallel Execution:
T2: LOCK(Y) → Process Y (parallel!)
T3: LOCK(Z) → Process Z (parallel!)
→ All CPU cores utilized!
💾 Problem 3: IO Lag
CPU Idle During Disk Access
Read Operations:
Rs = Read Start (CPU→Disk)
Re = Read End (Disk→CPU)
Gap = ~5ms of waiting
Write Operations:
Ws = Write Start (CPU→Disk)
We = Write End (Disk confirms)
Gap = ~10ms of waiting
✅ With Locks:
T2 uses CPU during T1's IO gaps
The Lock Cycle: How It Works 🔄
3 Transactions (T1, T2, T3) competing for 2 Concert Tickets (seat A, seat B)
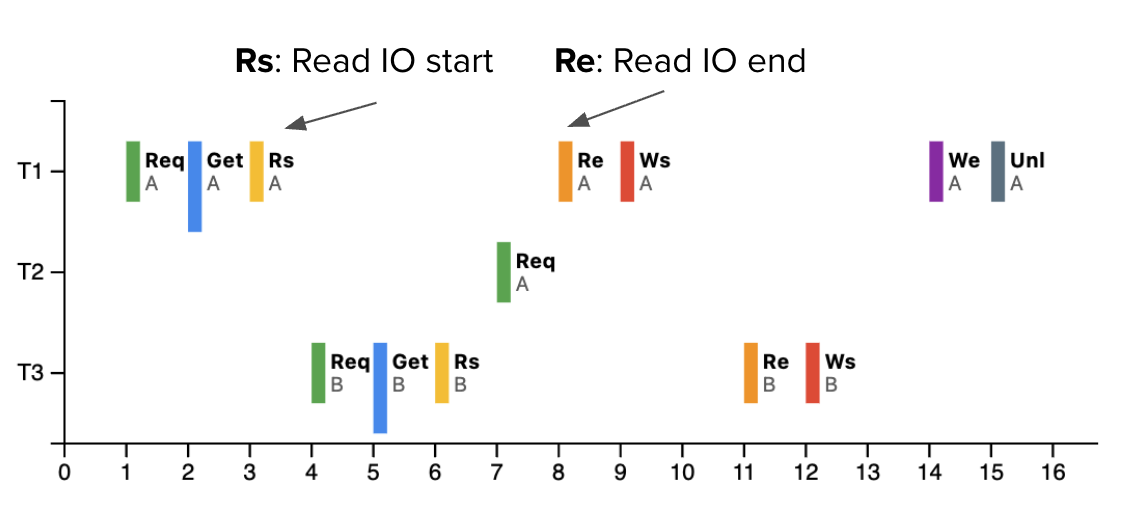
Key Insight: T1 and T3 can work simultaneously (different tickets), but T2 must wait for T1.
Legend: Operation Types
Step-by-Step Lock Lifecycle
During IO gaps (Rs→Re), locks coordinate access between T1, T2, T3:
1️⃣ Request
Transaction asks for lock on concert ticket
T3: REQ_LOCK(Ticket_B, lock)
2️⃣ Get
Lock manager checks who gets access
Waiting: T2 waits
3️⃣ Use Data
Read ticket data (IO) then process purchase (Logic)
Logic: Calculate total, apply discount
4️⃣ Unlock
Release lock so others can buy
After: We (write confirmed)
Types of Locks: Why We Need Two Kinds 🔐
The Opportunity: Reads vs Writes are Different
Key Insight: Reading doesn't change data, writing does. So we can optimize!
📖 Shared Lock (S-lock)
For Reading Data
Real Example: Checking Seat A-15 Availability
T2: S-LOCK(Seat_A15) → READ status = "available"
T3: S-LOCK(Seat_A15) → READ status = "available"
✅ All can check availability simultaneously!
Everyone can look at the same seat's status at once without interfering.
✏️ Exclusive Lock (X-lock)
For Writing Data
Real Example: Purchasing Seat A-15
T2: [BLOCKED] Can't even check availability
T3: [BLOCKED] Can't check or buy
🚫 Only one can buy (or even look) at a time!
During purchase, no one else can read OR write to prevent seeing partial updates.
Why This Design is Smart 🧠
🚀 Maximum Browsing
Multiple transactions can read the same data simultaneously (S + S = ✅)
Example: 1000 customers can check seat A-15's availability at the same time
🛡️ Purchase Integrity
No transaction can read while another is writing (S + X = ❌)
Example: When someone is buying seat A-15, others can't even check it (prevents seeing partial updates)
🔒 No Double-Booking
Only one transaction can write at a time (X + X = ❌)
Example: Only one person can complete purchase of seat A-15
Lock Compatibility Matrix
| 📖 Shared (S) | ✏️ Exclusive (X) | |
|---|---|---|
| 📖 Shared (S) | ✅ Compatible Many readers OK |
❌ Conflict No read during write |
| ✏️ Exclusive (X) | ❌ Conflict No write during read |
❌ Conflict Only one writer |
Example: Bank Transfer with IO Timing
-- Transaction: Transfer $100 from Account A to Account B
BEGIN TRANSACTION
-- Before Rs: Request locks
LOCK_EXCLUSIVE(Account_A) -- Granted instantly
LOCK_EXCLUSIVE(Account_B) -- Granted instantly
-- Trigger Rs→Re: Read operations
READ balance_A FROM Account_A -- Rs_A → ... → Re_A (balance_A = 500)
READ balance_B FROM Account_B -- Rs_B → ... → Re_B (balance_B = 200)
-- Process data (CPU time)
balance_A = balance_A - 100 -- Account_A = 400
balance_B = balance_B + 100 -- Account_B = 300
-- Trigger Ws→We: Write operations
WRITE(Account_A, 400) -- Ws_A → ... → We_A
WRITE(Account_B, 300) -- Ws_B → ... → We_B
-- After We: Release locks
UNLOCK(Account_A)
UNLOCK(Account_B)
COMMIT
Key Point: During the Rs→Re and Ws→We gaps, other transactions can acquire locks on different accounts and make progress!